My Publications: Antidepressants and Depression
CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 gene variants effects on antidepressant response, side effects, and blood concentrations
- Islam, F., et al. (2023). Effects of CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 gene variants on escitalopram and aripiprazole treatment outcome and serum levels: results from the CAN-BIND 1 study. Translational Psychiatry. [PDF]
-
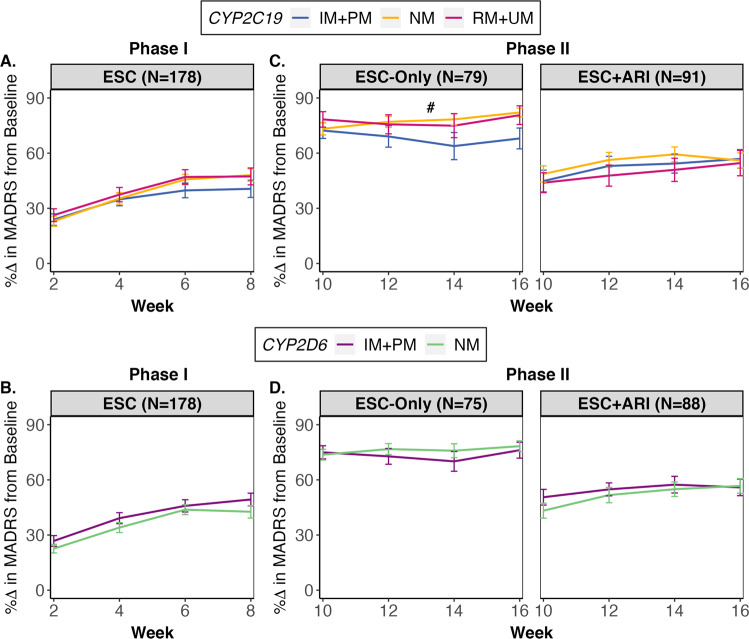
During Phase I, A CYP2C19 or B CYP2D6 metabolizer groups did not have a significant influence on symptom improvement over time. During Phase II, for the ESC-Only treatment arm, the average symptom improvement from baseline for every two-week assessment trended towards being lower in C CYP2C19 IM + PMs compared to NMs, which was not observed in the ESC + ARI group. There were no associations between symptom improvement over the course of Phase II and D CYP2D6 metabolizer groups for any of the treatment arms. All linear mixed effects analyses were adjusted for age, ancestry, sex, and interaction between time and CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 metabolizer groups as fixed effects, and recruitment site and subject as random effects variables. Error bars represent standard error.
ARI = aripiprazole, ESC = escitalopram, IM = intermediate metabolizer, NM = normal metabolizer, PM = poor metabolizer, RM = rapid metabolizer, UM = ultra-rapid metabolizer. # indicates trend with q between 0.050 and 0.070.
CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 gene variants effects on antidepressant-induced sexual side effects
- Islam, F., et al. (2024). Influence of CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and ABCB1 Gene Variants and Serum Levels of Escitalopram and Aripiprazole on Treatment-Emergent Sexual Dysfunction: A Canadian Biomarker Integration Network in Depression 1 (CAN-BIND 1) Study. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. [PDF]
-
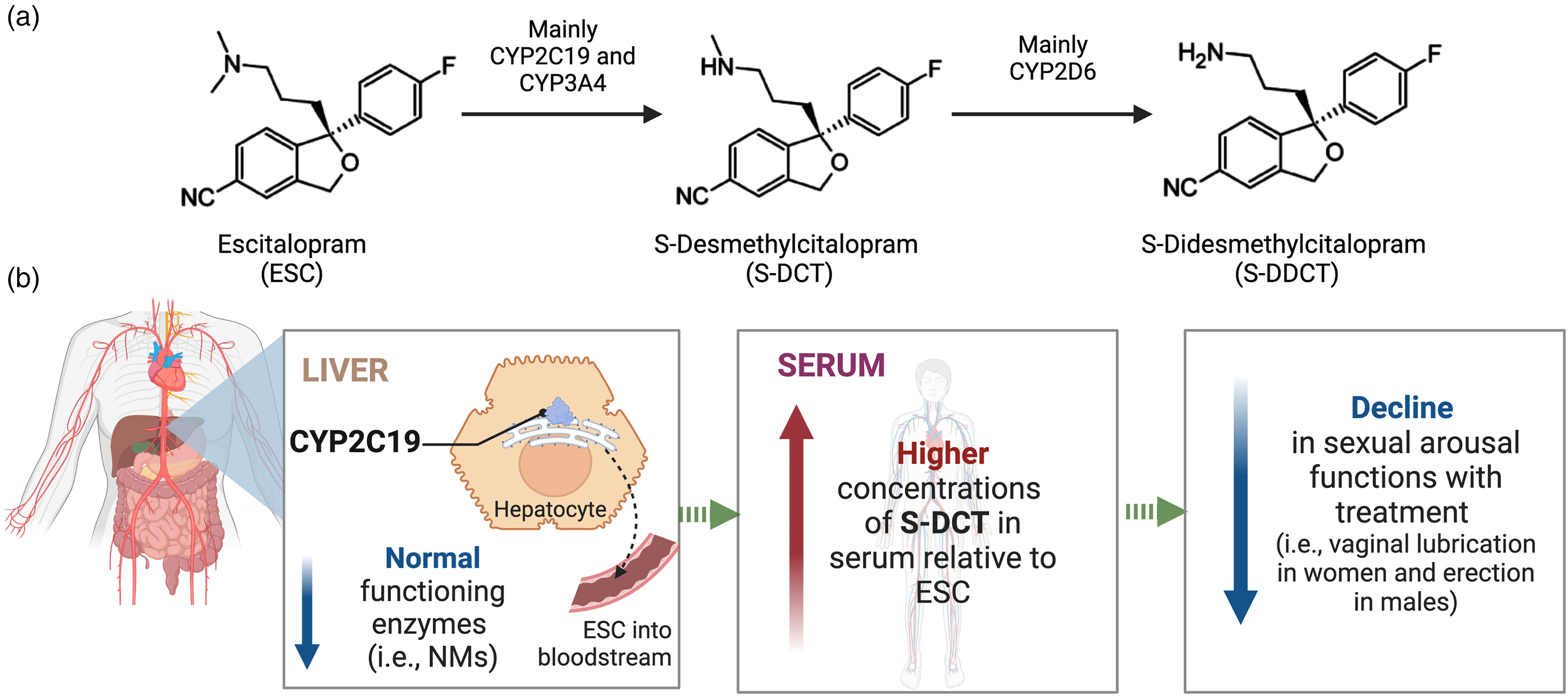
(a) ESC biotransformation pathway. (b) Genetic differences in the metabolism of ESC by CYP2C19 are expected to contribute to variations in treatment-emergent dysfunctions in sexual arousal that some patients on SSRIs experience. Specifically, individuals with gene variants contributing to elevated brain concentrations of S-DCT (i.e., CYP2C19 NMs), which itself is active as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor with potency comparable to the parent compound, are expected to have increased serotonin neurotransmission leading to enhanced inhibition of brain circuitry mediating sexual arousal. As a result, these individuals may experience more negative effects of the medication on their ability to have and sustain vaginal lubrication in females and erection in males.
ESC = escitalopram; NM = normal metabolizer; S-DCT = S-desmethylcitalopram.
Genetic variation, DNA methylation, and gene expression analysis of antidepressant response
- Islam, F., et al. (2024). Integrative Genetic Variation, DNA Methylation, and Gene Expression Analysis of Escitalopram and Aripiprazole Treatment Outcomes in Depression: A CAN-BIND-1 Study. Pharmacopsychiatry. [PDF]
-
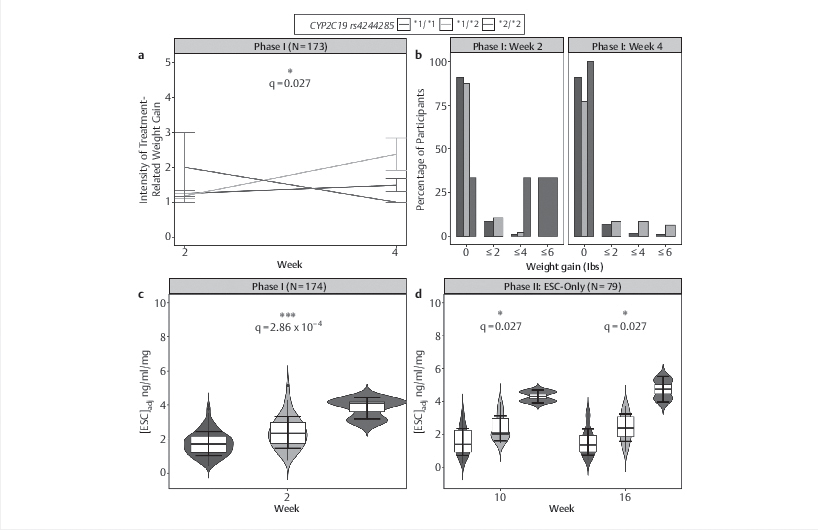
One significant mQTL SNP, CYP2C19 rs4244285, was associated with our outcomes of interest: (a-b) CYP2C19 rs4244285 was associated with treatment-related weight gain between weeks 2 to 4 dext-linkng Phase I with 6.7% and 14.9% of participants with the *1/*1 (n=119) and *1/*2 (n=47) genotypes, respectively, reporting ≥2 lbs of treatment-related weight gain, whereas none of those with the *2/*2 genotype (n=3) reported weight gain. (b-c) Relative to those with the *1/*1 genotype, those with the *1/*2 and *2/*2 genotypes of CYP2C19 rs4244285 showed higher ESCadj serum concentrations at weeks 2, 10, and 16 dext-linkng Phase I and in ESC-Only dext-linkng Phase II adjusted for age, ancestry, recruitment site, sex, and time since last ESC dose. Specifically, the *2/*2 group demonstrated the highest ESCadj concentrations with those having *1/*2 had concentrations between the two groups.
Note: ARI=Aripiprazole; ESC=Escitalopram; mQTLs=Methylation quantitative trait loci, the association between SNPs and methylation level; S-DCT=S-desmethylcitalopram.
© 2025, Farhana Islam